Regulations 3GPP2: A Foundation for Wireless Communication
Regulations 3GPP2: A Foundation for Wireless Communication
Blog Article
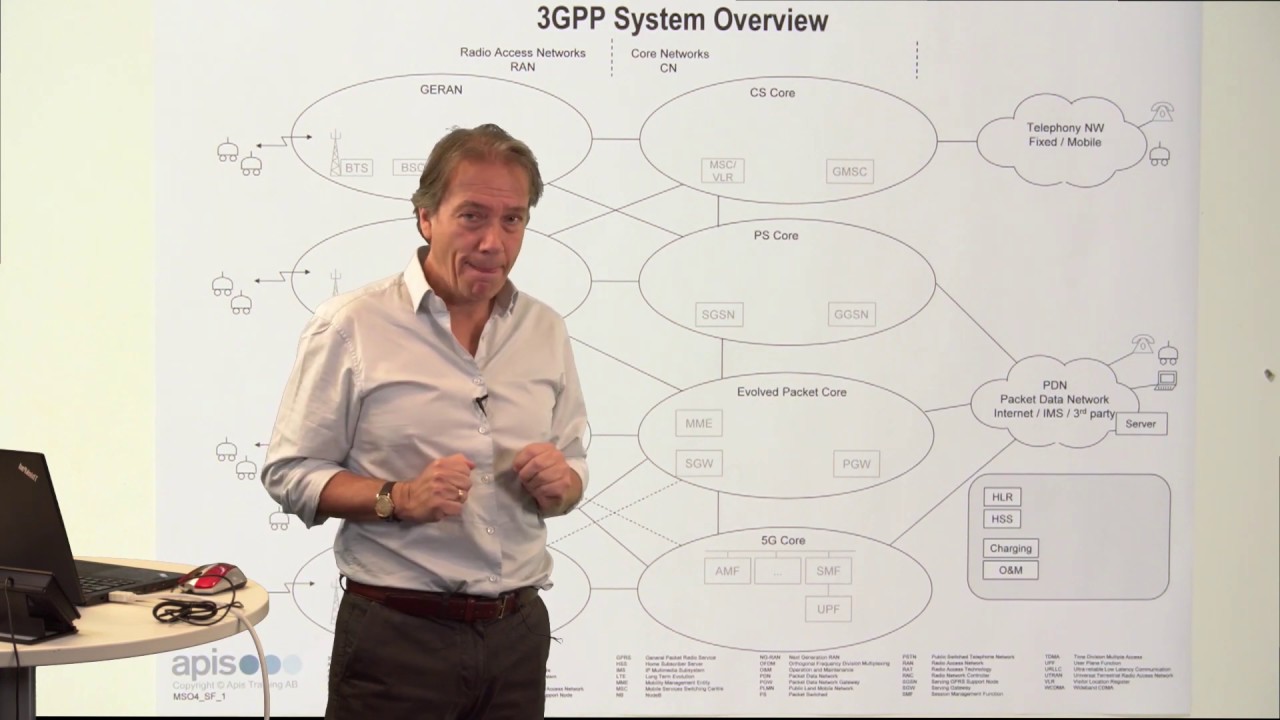
The sector of wireless communication relies heavily on robust and interoperable standards. Among these, the 3GPP2 specifications have fulfilled a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of mobile development. Developed by the Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2), these benchmarks primarily focus on the advancement and evolution of wireless communication networks operating in North America. By defining common interfaces, protocols, and functionalities, 3GPP2 standards ensure seamless connectivity between devices from different manufacturers, fostering a competitive and thriving ecosystem.
- Significantly, these standards encompass a wide range of technologies, including CDMA2000, EV-DO, and 1xRTT, which have been instrumental in delivering high-speed data, voice, and multimedia services to consumers. The ongoing evolution of 3GPP2 standards ensures that the wireless infrastructure remains agile and responsive to the ever-changing demands of users.
- Additionally, the standardization efforts within 3GPP2 regularly address emerging trends such as machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, Internet of Things (IoT), and the integration with next-generation networks.
Consequently, 3GPP2 standards have become an indispensable cornerstone for wireless communication in North America, enabling innovation, competition, and ultimately, enhanced user experiences.
Next-Gen CDMA2000: Elevating Data Transfer and Features
The evolution of CDMA2000 has been characterized by a continuous drive to improve data rates and expand the variety of available services. Building upon the robust foundation of its predecessor, CDMA2000 has experienced significant progresses that have led to a more versatile and capable wireless platform.
This evolutionary steps have emphasized on increasing data speeds to accommodate the ever-growing demand for high-speed internet access and multimedia applications.
Furthermore, CDMA2000 has a wider range of services, covering everything from voice calling and text messaging to video streaming and mobile gaming.
- This expansion in service offerings has CDMA2000 a truly well-rounded wireless communication solution.
EVDO Technology: Accelerating Mobile Broadband Access
EVDO technology/system/platform represents a significant leap/advancement/milestone in the evolution of mobile connectivity/broadband/internet access. This robust/powerful/advanced technology, based on CDMA principles/standards/guidelines, offers users/subscribers/customers significantly faster/higher/enhanced data speeds compared to its predecessors/antecedents/forerunners.
EVDO's capabilities/features/attributes include latency reduction/improved response times/shorter delays, enabling seamless streaming/browsing/downloads of multimedia content. Its extensive/wide/broad network coverage provides a reliable and consistent/stable/dependable connection across/throughout/over various geographic regions/locations/areas. With EVDO, mobile devices/gadgets/smartphones can access the internet with speeds that were once reserved for fixed-line/wired/land-based connections, transforming/revolutionizing/changing the way we communicate/interact/engage in a mobile/wireless/on-the-go world.
IS-2000 : Foundation to 3G CDMA Networks
IS-2000, a foundational standard in the evolution of wireless communication, paved the way for the widespread adoption of 3G CDMA networks. It introduced a robust framework for improved data rates and broader coverage compared to its predecessors. IS-2000's influence was significant, laying the basis for future generations of CDMA technology, including the highly efficient 3G networks that revolutionized mobile communication.
The standard's capacity to seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure TIA/EIA (Telecommunications Industry Association/Electronic Industries Alliance) was a key element in its success. IS-2000 also introduced important developments, such as channel allocation techniques, which optimized network efficiency.
CDMA2000 vs. EVDO
Comparing CDMA 1x and EVDO technologies highlights the evolution of mobile broadband capabilities. While both utilize a Code Division Multiple Access principle, EVDO represents a significant advancement in data transfer speeds and overall network capacity. CDMA2000 provides basic voice and slower data services, making it suitable for developing markets. However, EVDO dramatically increases data rates, enabling applications like video streaming and mobile browsing seamlessly. This evolution reflects the ever-growing demand for faster and more versatile wireless connectivity.
Grasping 3GPP2's Part in Wireless Specifications
The Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2) is a prominent group dedicated to developing and promoting wireless communication regulations. It plays a essential role in shaping the landscape of mobile technology by establishing specifications for various aspects of wireless communication, including radio access technologies, network protocols, and security mechanisms. 3GPP2's contributions have had a profound impact on the evolution of wireless networks, particularly in North America, where its standards are widely utilized.
How CDMA2000 Shaped the Wireless Market
CDMA2000 sprung up as a significant development in the mobile industry during the late 1990s. This system offered enhanced network capacity and spectral efficiency, allowing for an increased number of users to connect simultaneously. CDMA2000's implementation caused a shift in the mobile landscape, encouraging a development of data services and altering user interactions.
- Furthermore, CDMA2000's robustness enabled it as a viable choice for both urban and countryside areas.
- As a result, CDMA2000's influence on the mobile industry was substantial.
Rolling out EVDO Networks for Optimal Performance
Achieving optimal performance in EVDO deployments requires a strategic approach. Network optimization strategies should focus on maximizing data throughput and minimizing latency, taking into account factors like antenna placement, channel bandwidth allocation, and user density. Rolling out a tiered network architecture with dedicated coverage areas for various traffic types can further enhance performance. Moreover, regular monitoring and analysis of network parameters are crucial to identify bottlenecks and implement proactive adjustments.
- Leveraging advanced scheduling algorithms can enhance resource allocation, ensuring efficient use of bandwidth.
- Rollout of robust Quality of Service (QoS) policies can prioritize critical traffic types, guaranteeing a seamless user experience.
- Implementing dynamic power control mechanisms can minimize interference and extend network coverage.
Enhancing Data Transmission with EVDO Rev. A
Evolution-Data Optimized (EVDO) Revision A represents a significant leap forward in wireless data transmission technology. This revamped version of the EVDO standard provides increased speeds and capacity, enabling a more seamless and efficient user experience. By leveraging sophisticated modulation techniques and sophisticated antenna systems, EVDO Rev. A reaches data rates up to 3.1 Mbps, significantly surpassing the capabilities of its predecessor. This enhancement in performance allows for faster downloads, smoother video streaming, and more dependable data connectivity.
Challenges and Possibilities in 3GPP2 Standardization
The realm of mobile networks constantly evolves, presenting both substantial opportunities and complexities for standardization efforts. 3GPP2, a key organization driving the evolution of CDMA-based technologies, addresses a myriad of problems in its quest to guarantee interoperability and progress within this dynamic landscape. Continuously evolving user requirements, the emergence of new technologies, and the need for coherent integration across diverse systems present considerable challenges to 3GPP2's standardization process.
- Additionally, balancing the needs of diverse stakeholders, including carriers, device manufacturers, and regulatory bodies, can prove a challenging undertaking.
- Despite these difficulties, 3GPP2 also stands at the forefront of several exciting scenarios.
- Specifically, the integration of 5G technologies into existing CDMA networks offers the potential for improved capacity, performance, and reliability.
Ultimately, navigating the challenges and capitalizing the opportunities presented by 3GPP2 standardization is critical for the continued advancement of the wireless communications industry.
Legacy Networks Keeping CDMA2000 Relevant
Despite the rise of advanced wireless technologies, CDMA2000 persists a significant player in certain regions and sectors. Operators are strategically implementing strategies to extend the lifespan of their CDMA2000 networks. This includes allocations in network upgrades, application modernization, and research into interoperability with contemporary technologies. While CDMA2000 may not be the primary technology of the future, it continues to provide reliable communications for a substantial user base.
- Notable features of CDMA2000 include its robustness, security, and wideband capabilities.
- Migrating users to newer technologies can be a challenging process.
- System upgrades are crucial for extending the lifespan of CDMA2000 networks.